5 Interesting Command Line Tips and Tricks in Linux – Part 1
Are you making most out of the Linux? There are lots of helpful features which appears to be Tips and Tricks for many of Linux Users. Sometimes Tips and Tricks become the need. It helps you get productive with the same set of commands yet with enhanced functionality.
Here we are starting a new series, where we will be writing some tips and tricks and will try to yield as more as we can in small time.
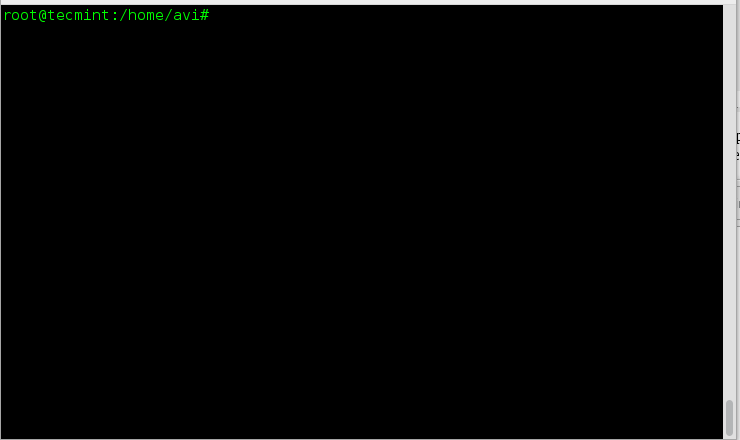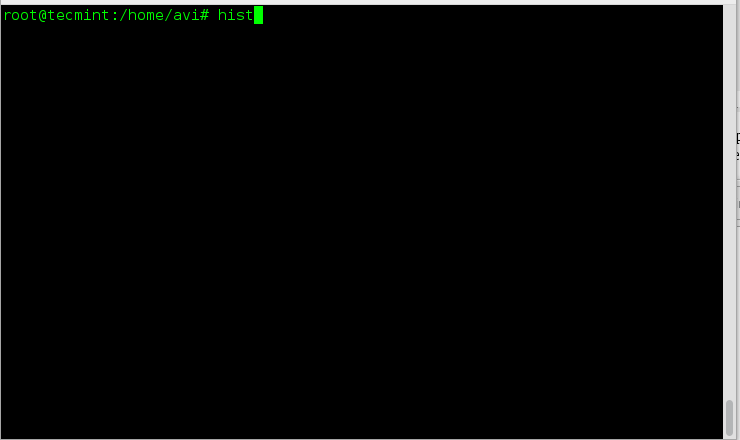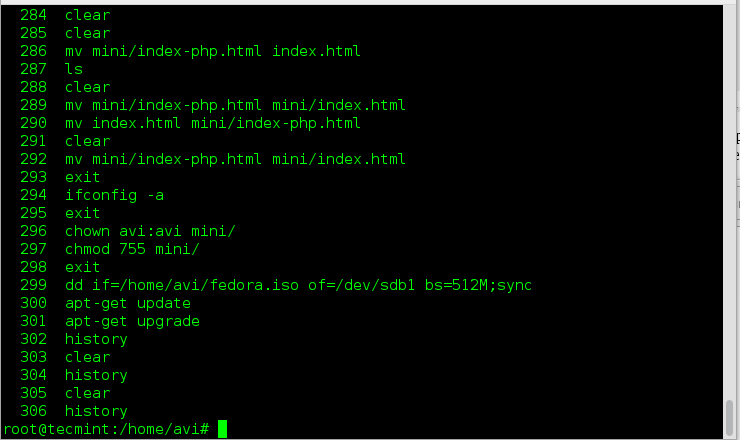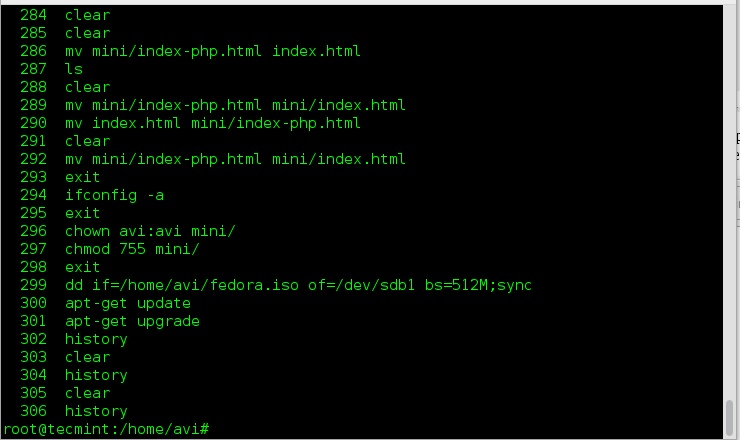
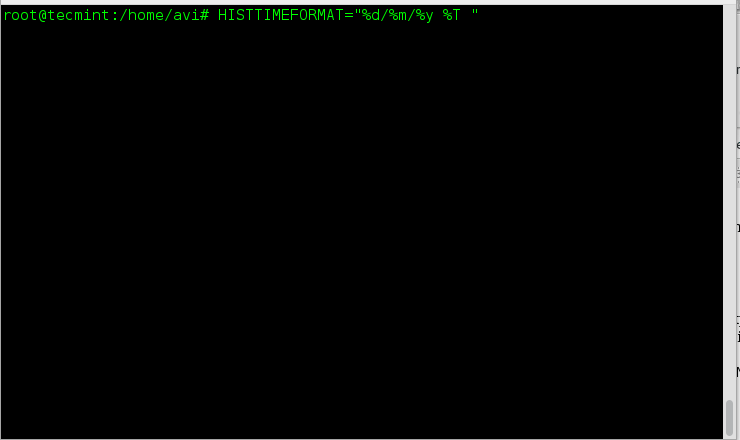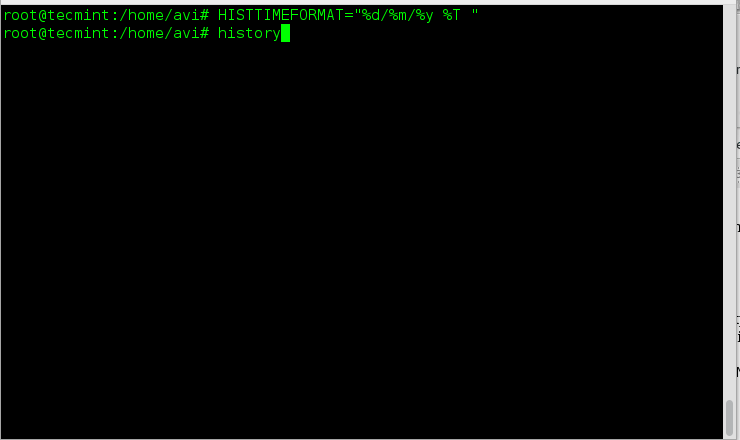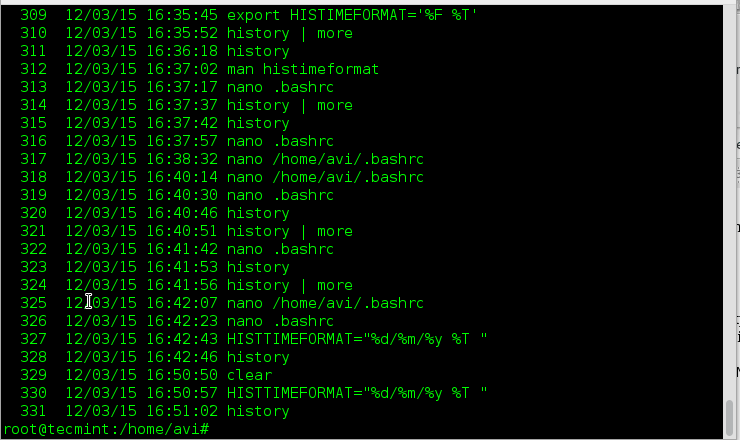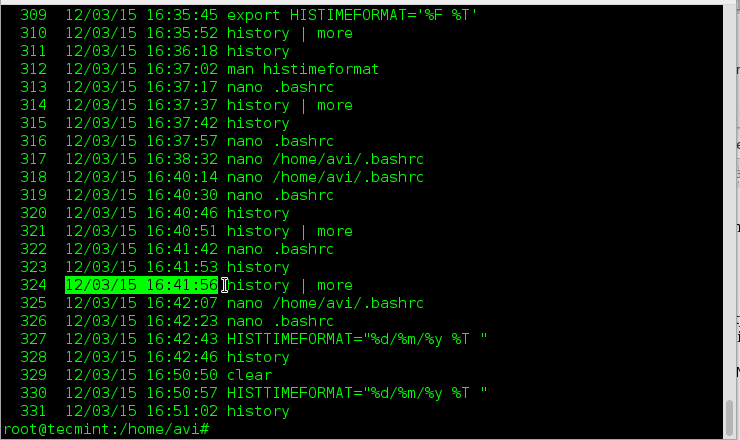
1. To audit the commands we’d run in past, we use history command. Here is a sample output of history command.
Obvious from output, the history command do not output the time stamp with the log of last executed commands. Any solution for this? Yeah! Run the below command.
If you want to permanently append this change, add the below line to
~/.bashrc.
and then, from terminal run,
Explanation of commands and switches.
- history – GNU History Library
- HISTIMEFORMAT – Environmental Variable
- %d – Day
- %m – Month
- %y – Year
- %T – Time Stamp
- source – in short send the contents of file to shell
- .bashrc – is a shell script that BASH runs whenever it is started interactively.
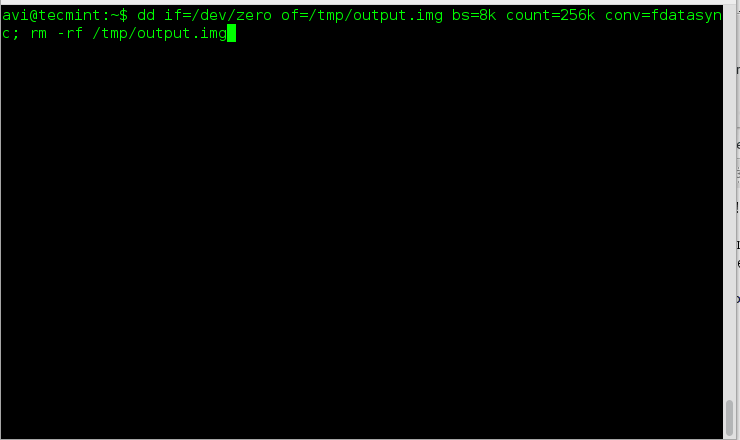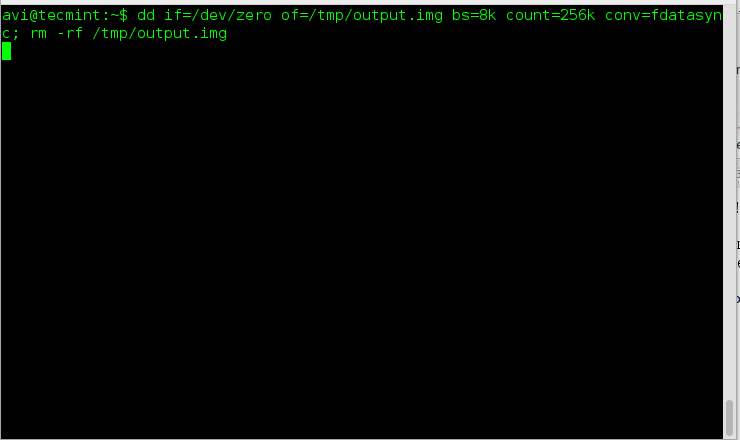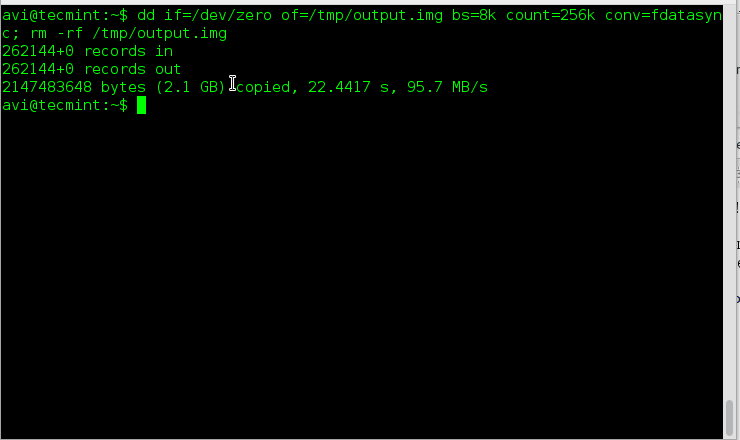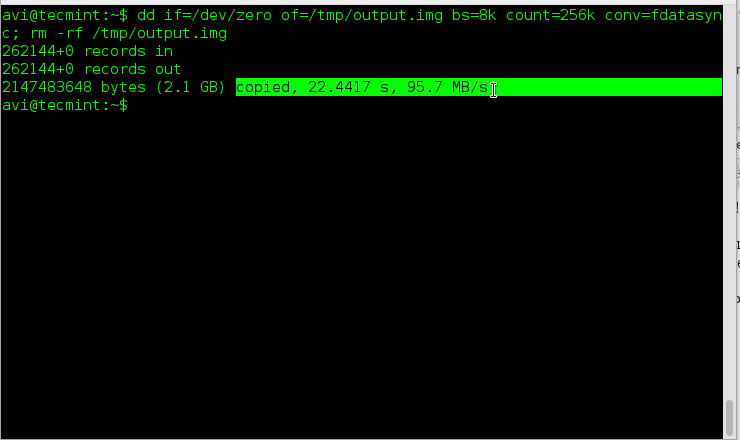
2. The next gem in the list is – how to check disk write speed? Well one liner dd command script serves the purpose.
Explanation of commands and switches.
- dd – Convert and Copy a file
- if=/dev/zero – Read the file and not stdin
- of=/tmp/output.img – Write to file and not stdout
- bs – Read and Write maximum upto M bytes, at one time
- count – Copy N input block
- conv – Convert the file as per comma separated symbol list.
- rm – Removes files and folder
- -rf – (-r) removes directories and contents recursively and (-f) Force the removal without prompt.
3. How will you check the top six files that are eating out your space? A simple one liner script made from du command, which is primarily used as file space usages.
Explanation of commands and switches.
- du – Estimate file space usages
- -hsx – (-h) Human Readable Format, (-s) Summaries Output, (-x) One File Format, skip directories on other file format.
- sort – Sort text file lines
- -rh – (-r) Reverse the result of comparison, (-h) for compare human readable format.
- head – output first n lines of file.
4. The next step involves statistics in terminal of a file of every kind. We can output the statistics related to a file with the help of stat (output file/fileSystem status) command.
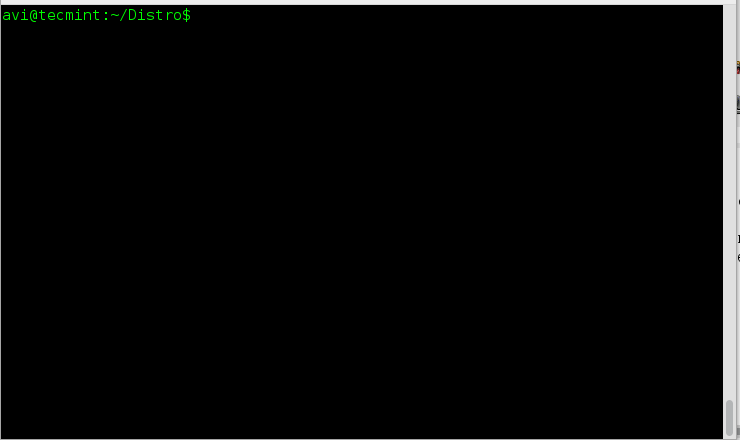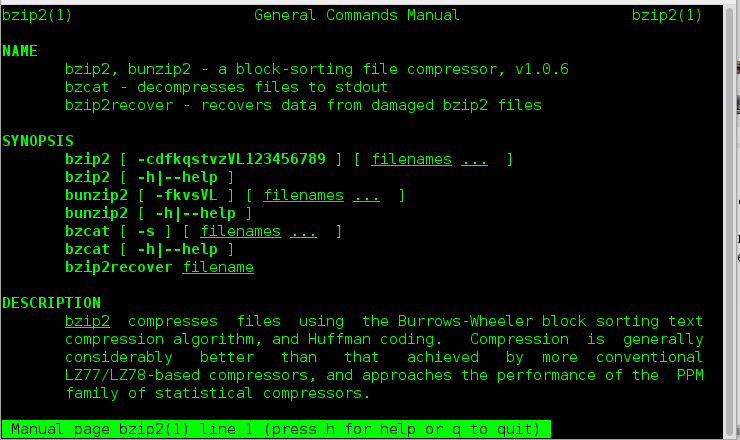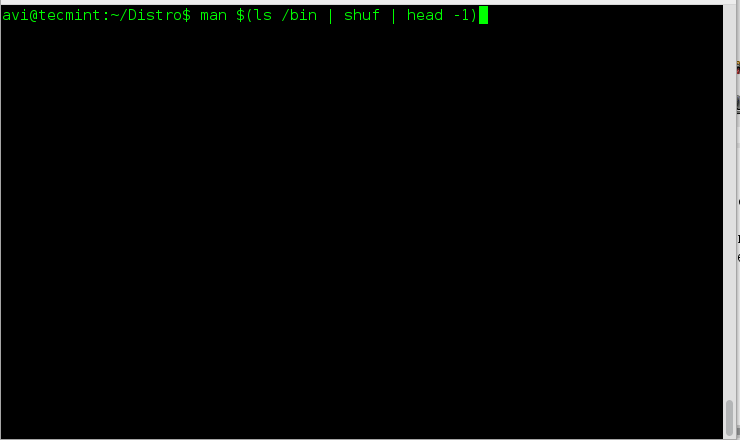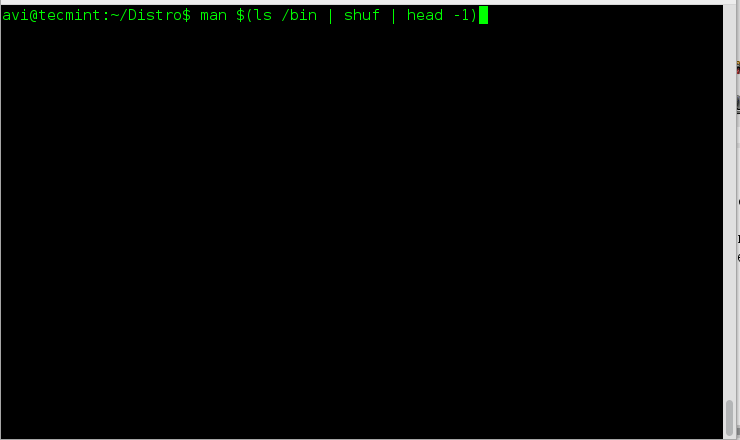
5. The next and last but not the least, this one line script is for those, who are newbies. If you are an experienced user you probably don’t need it, unless you want some fun out of it. Well newbies are Linux-command-line phobic and the below one liner will generate random man pages. The benefit is as a newbie you always get something to learn and never get bored.
Explanation of commands and switches.
- man – Linux Man pages
- ls – Linux Listing Commands
- /bin – System Binary file Location
- shuf – Generate Random Permutation
- head – Output first n line of file.



No comments:
Post a Comment